Management Policies & Systems
Corporate Governance
Basic Corporate Governance Policy
The Mitsubishi Electric Group places more focus than ever on sustainability initiatives at the management level to realize "a vibrant and sustainable society" that we have committed to in our Purpose. The Group has identified five areas as materiality (important challenges) to "provide solutions to social challenges through our businesses" and to "strengthen our business foundation to enable sustainable growth." Through these materiality initiatives, the Group will create economic and social value and will contribute to solving social challenges.
As a part of our initiatives to strengthen our business foundation to enable sustainable growth, the Group recognizes the importance of corporate governance as a fundamental precondition for our continued existence. The Group’s fundamental policy is to further enhance its corporate value by constructing, maintaining, and sustainably strengthening a corporate governance system that more accurately meets the expectations of society, our customers, shareholders, employees, and all other stakeholders.
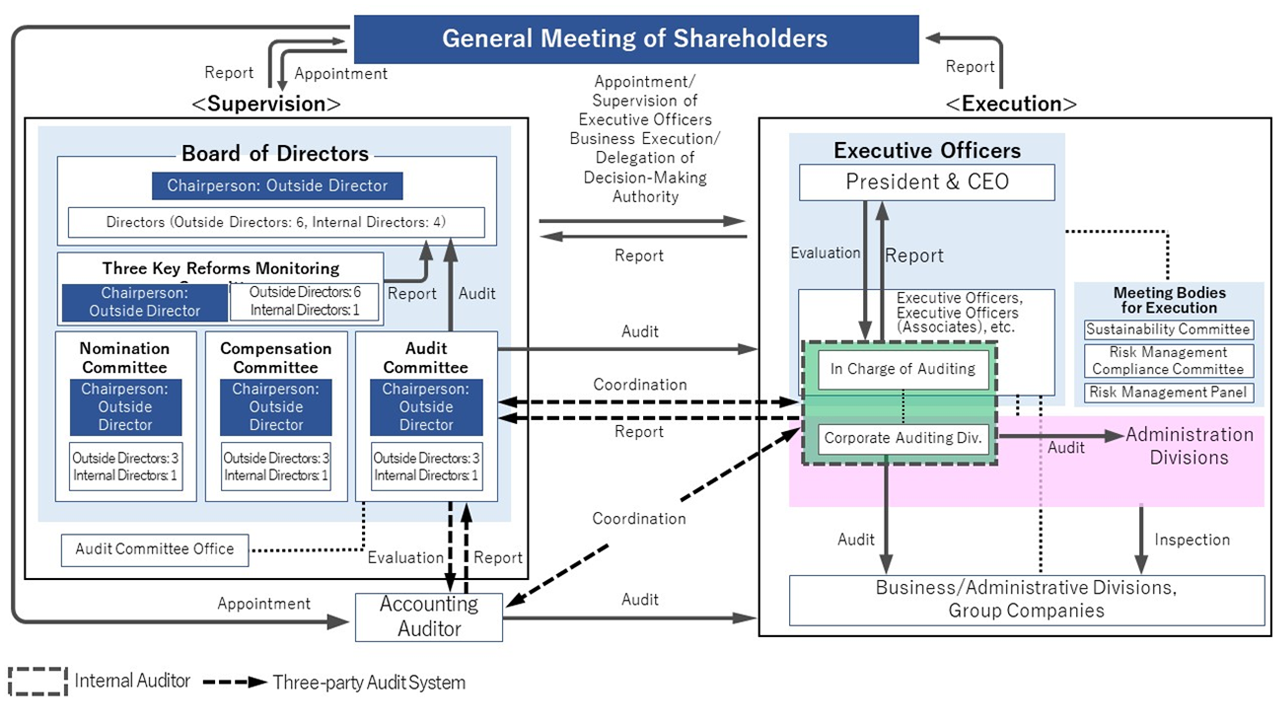
As a company with a three-committee system, the Company segregates the supervisory and executive functions; the Board of Directors plays a supervisory decision-making role and Executive Officers handle the day-to-day running of the Company. This system maintains the flexibility of its operations and promotes management transparency, leading to swift and decisive management decision-making. Through this system, the Company aims to promote sustainable growth in corporate value. To this end, the Company recognizes the importance of a highly independent Board of Directors adequately fulfilling its roles and responsibilities in corporate governance as a supervisory function.
The Board of Directors formulates and publishes Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Corporate Governance Guidelines based on the views outlined above. The purpose of the Guidelines is to promote a clear understanding of the fundamental approach and framework of corporate governance and to build long-lasting, mutually trusting relationships through constructive dialogue with shareholders. The Board will inspect and review the Guidelines on an ongoing basis to ensure that the basic policy is effectively implemented and enhance our corporate governance practices.
In regard to compliance with the Corporate Governance Code established by the Tokyo Stock Exchange (issued in June 2021), "Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Initiatives to Comply with the Corporate Governance Code" is disclosed based on the Corporate Governance Guidelines.
This Corporate Governance Report contains the Company’s corporate governance policies and information for the fiscal year, in accordance with the format prescribed by the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Corporate Governance Guidelines
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Initiatives to Comply with the Corporate Governance Code
Corporate Governance Report
Implementation Status of Corporate Governance
Corporate Management Structure
Mitsubishi Electric has chosen to have a Three-committee system in place. The Company segregates the supervisory and executive functions; the Board of Directors plays a supervisory decision-making role and Executive Officers handle the day-to-day running of the Company. This system improves flexibility of its operations and promoting management transparency, leading to swift and decisive management decision-making, therefore the Company aim to promote sustainable growth in corporate and shareholder values.
To promote the segregation of supervisory and executive functions, which is the characteristic of this system, the Company’s Board of Directors shall be dedicated to supervising management with specific details of deliberations stipulated as the Board of Directors' deliberation criteria. By delegating to the Executive Officers, the authority to make all business execution decisions within the limits permitted by the Companies Act, the Company ensure swift and decisive decision-making and appropriate risk-taking in business execution.
Both the Board of Directors and the three statutory committees shall be chaired by independent outside directors, and a majority of their members shall be independent outside directors as well, thereby improving the effectiveness of the supervisory function.
In addition, the Executive Officers’ Meeting shall be established as a voluntary body to deliberate and make decisions on important business matters from the perspective of pursuing synergy and multifaceted risk management, in addition to sharing information among Executive Officers.
Corporate Governance Framework
Internal Control System
1.
For the execution of the duties of the Audit Committee, its independence is secured by assigning employees whose job is exclusively to assist the Audit Committee members. In addition, internal regulations regarding the processing of expenses and debts incurred in the execution of the duties of the Audit Committee members are established and such expenses and debts are properly processed.
A system for reporting to the Audit Committee is developed to report information about the Company and its subsidiaries to the Audit Committee via the divisions in charge of internal control, and an internal whistle-blower system is developed and its details are reported to the Audit Committee members.
Furthermore, the Audit Committee members attend important meetings including Executive Officers' meetings and conduct investigations such as interviews with Executive Officer and the executives of the Company’s offices and subsidiaries, and undertake deliberations to determine audit policies, methods, implementation status, and results of the audit by regularly receiving reports from the Independent Auditor and the Executive Officer or the Senior Executive Officer in charge of auditing.
2.
Internal regulations and systems to ensure the properness of operations within the Mitsubishi Electric Group are established. Executive Officers take responsibility for constructing such systems within the areas over which they are appointed. Important matters are deliberated by convening Executive Officer meetings.
Executive Officers regularly monitor the status of management of the systems. The divisions in charge of internal control monitor the status of design and management of internal control system and regulations. Also an internal whistle-blower system is developed and its details are reported to the Audit Committee members.
Furthermore, the status of management of the system is audited by internal auditors, and the audit results are reported regularly to the Audit Committee via the Executive Officer or the Senior Executive Officer in charge of auditing.
Upon receipt of the Governance Review Committee’s recommendation on improper quality control practices, the Board of Directors will deliberate again on the resolution, including whether or not the decision should be revised.
Audit Committee
1. Organization, Members, and Procedures of the Audit Committee
The Audit Committee is made up of five Director, three of whom are Outside Director. The Committee audits the legality, adequacy, and efficiency of the execution of the duties by Director and Executive Officers and creates an audit report to be submitted to the shareholders’ meeting with its resolution.
Kazunori Watanabe, a member of the Audit Committee, is a Certified Public Accountant and has a considerable degree of knowledge about finance and accounting. Tadashi Kawagoishi, a member of the Audit Committee, has long years of experience in the accounting and financial operations of the Company.
The Audit Committee has four dedicated staffers who take direct orders from Audit Committee members and support them in executing their duties.
2. Frequency of the Audit Committee meeting and attendance of each Director
The Company held fourteen Audit Committee meetings during the fiscal year. Each meeting took about one and a half hours. Audit Committee members worked to secure sufficient time for questions and answers on the day of the Audit Committee meeting, such as by checking materials with audio commentary in advance through the Audit Committee website, mainly for matters for reporting. The attendance of each Audit Committee member is as shown below.
| Title | Name | Attendance/meetings | Attendance rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman of the Audit Committee (Outside Director) |
Hiroyuki Yanagi | 11/11 | 100% |
| Member of the Audit Committee (Outside Director) |
Kazunori Watanabe | 14/14 | 100% |
| Member of the Audit Committee (Outside Director) |
Haruka Matsuyama | 11/11 | 100% |
| Member of the Audit Committee |
Tadashi Kawagoishi | 14/14 | 100% |
| Member of the Audit Committee |
Jun Nagasawa | 14/14 | 100% |
Notes
- 1. Out of the above members, Messrs. Tadashi Kawagoishi and Jun Nagasawa are responsible for investigation.
- 2. The status of attendance for Mr. Hiroyuki Yanagi and Ms. Haruka Matsuyama is based on the number of the Audit Committee meetings held after their assumption of office on June 29, 2023.
- 3. Messrs. Kazunori Watanabe, Tadashi Kawagoishi and Jun Nagasawa retired upon the expiration of their terms of office at the end of the 153rd Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders held on June 25, 2024.
3. Activities of the Audit Committee Members
- The Audit Committee members–mainly those responsible for investigation (full-time Audit Committee members)–attend Executive Officers' meetings and other such important conferences, and conduct investigations such as interviews with Executive Officers and Executive Officers (Associate), as well as visits of the Company’s offices and subsidiaries and interviews with executive staff thereof in accordance with the policies and assignments agreed upon the Committee.
- The Audit Committee members receive internal audit reports and monthly reports from the Corporate Auditing Division. At Audit Committee meetings, members also receive reports on internal audit policies for the fiscal year and the results of semi-annual internal audits, and provide their opinions as necessary.
- The Audit Committee members receive reports from the Corporate Legal & Risk Management Group and other departments in charge of internal control, such as reports on the building of an internal control system that emphasizes predictive indicators and prevention, the formulation and operation of a compliance program, and the development and operation of an internal whistle-blowing system, and provide their opinions as necessary.
- The Audit Committee members discuss policies and methods of auditing with Independent Auditors, who furnish them with quarterly reports on the implementation status of reviews, including responses to audit risks, and explanations of their quality management system and independence, and exchange opinions with them.
In addition, Outside Audit Committee members visit the Company’s offices and subsidiaries to offer their opinions based on the various skills they each possess at the Audit Committee meeting and other occasions.
4. Specific Agenda Contents of the Audit Committee
The specific agenda of the Audit Committee includes the formulation of audit policies and activity planning, checks on the status of execution of the duties by Directors and Executive Officers and the status of establishment and operation of the internal control system, checks on methods of auditing by the Independent Auditor and validity of results, and evaluation of the Independent Auditor and drafting of proposals for reappointment and non-reappointment of the Independent Auditor.
In fiscal 2024, the Audit Committee focused on monitoring and verifying various measures to address quality issues and to prevent the recurrence of labor and information security issues that have occurred in recent years. At the same time, the Audit Committee conducted interviews with and expressed its opinions to Executive Officers, Executive Officers (Associate), and the executive staff of the Company’s offices and subsidiaries as necessary on matters such as the status of efforts for initiatives aimed at sustainably increasing the Mitsubishi Electric Group’s corporate value and fulfilling its responsibilities to stakeholders, namely the promotion of sustainability management, the acceleration of portfolio strategies and business transformation under the new business area management structure, and strengthening the business structure, including the building of an internal control system that emphasizes prediction and prevention, and the formulation and operation of a compliance program.
The Group is focusing on accelerating its transformation to realize its ideal vision (Circular Digital-Engineering Company), strengthening its business structure, promoting material sustainability management, deepening and developing the three key reforms, and thoroughly instilling legal and ethical compliance. The Audit Committee will closely monitor the permeation of these initiatives throughout the Group, along with the various recurrence prevention initiatives being implemented by the Company, including efforts to prevent improper quality control practices as well as work-related and cybersecurity issues identified thus far from being forgotten.
5. Effectiveness Evaluation of the Audit Committee
The Audit Committee conducts evaluation to improve performance every year in the form of questionnaires to be filled out by each committee member. In fiscal 2024, the following opinions and proposals were made:
- The frequency of Audit Committee meetings, explanations of proposals, and Q&A sessions are sufficient and appropriate. Operations could be improved by setting key agenda items and providing materials in an even more timely manner.
- The Audit Committee members responsible for investigation (full-time Audit Committee members) periodically report their activities and the results thereof, and management information is properly shared among Audit Committee members in a timely manner.
Although we believe that these evaluations in effect endorse the performance of the Audit Committee, we will continue to make efforts to improve performance.
Status of Internal Audit
1. Organization, Members, and Procedures for Internal Audit
An internal audit is intended to contribute to the sound management and strengthened management structure of the Company and its affiliates in Japan and overseas by improving management efficiency, strengthening risk management, thoroughly observing the code of corporate ethics and ensuring compliance, and enhancing internal control.
With approximately 60 members acting independently in Japan and overseas, the Company’s Corporate Auditing Division conducts internal audits of the Company from a fair and impartial standpoint. In addition, the division's activities are supported by auditors with extensive knowledge of their particular fields, assigned from relevant business units.
2. Relationship with the Divisions in Charge of Internal Control
In the Group, the corporate management divisions and corporate staff groups such as the Corporate Strategic Planning Division, the Corporate Accounting Division, the Corporate Legal & Licensing Division, and the Corporate Export Control Division inspect the establishment and operation of the internal control system and regulations, etc. under their scope of responsibility for internal control. In addition, each business division has its own compliance department, which reliably spreads companywide compliance policies and inspects the compliance status in each business division.
The Corporate Auditing Division internally audits the operation and other aspects of the internal control system, evaluates the internal control related to the financial review, and mutually exchanges necessary information with each division in charge of internal control.
3. Mutual Relationship Among Internal Audit, the Audit by the Audit Committee, and Accounting Audit
The Corporate Auditing Division reports the internal audit policies and internal audit results to the Audit Committee and exchanges opinions with the Audit Committee members on a regular basis.
The Corporate Auditing Division also reports internal audit results to the Independent Auditors and continuously works with them, discussing the evaluation of the internal control related to financial review as needed.
4. Activities to Ensure the Effectiveness of Internal Audits
The Corporate Auditing Division prepares and sends an audit report to the head of the audited department after the internal audit is conducted, and instructs the head of the audited department to formulate improvement measures as necessary. In order to ensure the effectiveness of internal audits, the Corporate Auditing Division confirms the improvement measures developed by the audited department through the written responses submitted by the audited department, and conducts follow-up audits and evaluations to confirm the implementation progress as necessary.
In addition, the Corporate Auditing Division prepares a report summarizing the internal audit for the first and second half of the year as a regular report, and reports it, via the Executive Officers (Associate) in charge, to the Audit Committee, and the President & CEO twice a year.
Providing Directors with Appropriate Information at the Appropriate Time, and Conducting Reviews of the Board with Analyses and Evaluations
The Company requested Board Advisors, Inc., a third-party organization, to assess the effectiveness of the Board of Directors of the Company from July to September 2023.
A summary of the assessment method and process of the third-party organization is as follows.
Assessment Methods/Processes by the Third-party Organization
- (1) Assessment Methods
- (a) Review the minutes of the Board of Directors meetings and other documents
- (b) Survey of all Directors (excluding two new independent outside directors)
- (c) Interviews with all Directors
- (d) Evaluation based on the expertise of the third-party organization
- (2) Target Items of Assessment
- (a) Overall assessment
- (b) Composition of the Board of Directors
- (c) Support system of the Board of Directors
- (d) Agenda for Meetings of the Board of Directors
- (e) Status of Deliberations at Meetings of the Board of Directors
- (f) Contribution of Directors
- (g) Activities of the three statutory committees
- (h) Monitoring system of the Executives
- (3) Assessment Process
- (a) Conduct an assessment by a third-party organization based on (1) Assessment methods and (2) Target items of assessment
- (b) Report on the assessment results on the effectiveness of the Board of Directors based by the third-party organization to the Company’s Board of Directors
- (c) Conduct discussions by the Board of Directors on future actions based on the above assessment report
The summary of the assessment results on the Board of Directors’ effectiveness based on the third-party organization is indicated as follows.
- The effectiveness of the Board of Directors has generally been ensured. Progress has also generally been made on the issues cited in the evaluation of the effectiveness of the Board of Directors in fiscal 2023.
- The effectiveness of the Board of Directors is supported by the following strengths:
- (a) Commitment to continued reform
- (b) Enhancement of the composition of the Board of Directors
- (c) Elevation of the discussions at Board of Directors meetings
- On the other hand, new issues have also emerged, and the Board of Directors is expected to address the following key issues in order to achieve overall optimization and enhance corporate value.
- (a) Further enhancement of monitoring
- (b) Strengthening Group governance
- (c) Strengthening Board of Directors and committee agendas
Based on these evaluation results and the recommendations of the Governance Review Committee, the Company's Board of Directors will discuss measures to improve effectiveness, and then focus on "improving the management of the Board of Directors" to further strengthen the management monitoring function from an external perspective.
We will continue reviews of the Board and strive to further improve of the effectiveness of the Board of Directors.
Policies Regarding Decisions on Compensation, etc.
a. Basic Policies
- As a Company with a Three-committee System, the Company segregates the supervisory function and the execution function of management. The supervisory function of management is assigned to the Directors and the Board of Directors and the execution function of management is assigned to the Executive Officers. The compensation scheme for Directors and the compensation scheme for the Executive Officers will be set differently, corresponding to the contents and responsibilities of each duty and position. The compensation will be determined by the Compensation Committee based on the following basic policies:
- (a) Directors
- (i) The compensation scheme should encourage the Directors to demonstrate their supervisory function of management.
- (ii) The compensation should be the amount necessary to secure suitable talent to fulfill the responsibilities of the Company’s Directors.
- (b) Executive Officers
- (i) The compensation scheme should observe the corporate philosophy of the Mitsubishi Electric Group, and be fully accountable to all stakeholders including society, customers, shareholders, and employees.
- (ii) The compensation scheme should encourage the execution of duties in line with management strategies and provide strong incentives to achieve management goals.
- (iii) The compensation scheme should function as an incentive for sustained performance growth and the improvement of corporate value.
- (iv) The compensation scheme should reflect a fair and impartial evaluation of the achievements and contributions toward their respective roles and responsibilities.
b. The system for determining compensation
- (a) Directors
The compensation scheme for Directors shall consist exclusively of basic compensation (fixed compensation), in light of the Directors’ role to provide advice and supervise management from an objective and independent perspective. - (b) Executive Officers
The compensation scheme for Executive Officers shall be as follows, with an emphasis on the improvement of medium-term corporate value and shareholder value.- (i) Basic compensation
Fixed compensation is set in accordance with the roles and responsibilities of each Executive Officer and is paid monthly in cash by dividing the position-based annual standard amount by 12. - (ii) Performance-based bonus
The performance-based bonus consists of “Corporate Performance Evaluation” and “Individual Evaluation.” Toward the implementation and achievement of targets of important indicators, priority measures, etc. in the Medium-term Management Plan, the consolidated revenue, consolidated operating profit ratio, operating cash flow, and ROE are used as evaluation indicators for “Corporate Performance Evaluation.” For “Individual Evaluation,” as an evaluation indicator, non-financial targets and business areas are determined for each Executive Officer. For Executive Officers who control a Business Area or Business Group, actual results of their Business Group as well as non-financial targets are used as evaluation indicators. The amount to be paid is determined in accordance with the status of achievements of these indicators. The payment amount for each individual will fluctuate in the range of 0% to 200% and shall be calculated as below and paid in a lump sum in cash after the end of each fiscal year.
[Individual payment amount = Position-based standard amount x (Corporate performance evaluation coefficient + Individual evaluation coefficient) (in the range of 0-200%)] - (iii) Performance-based stock compensation (Performance Share Units (PSU))
In principle, the number of shares to be issued as performance-based stock compensation (PSU) varies between 0% and 200%, depending on the comparison result (in percentile) between the Company’s TSR (total shareholder return) for the three years and the TSR of a pre-selected group of comparable companies. The comparable companies are selected from domestic and overseas companies in the business areas in which the Company operates. The number of shares to be delivered to each individual is calculated as follows:
[Number of shares delivery to each individual =
Standard PSU points for the position × PSU grant rate (in the range of 0-200%)] - (iv) Restricted Stock Units (RSU)
In order to promote continuous shareholding and shareholder value during the term of office, the Restricted Stock Unit (RSU) program shall, in principle, deliver shares, with transfer restrictions, equivalent to the standard amount for the position at the end of each fiscal year. The transfer restrictions shall be lifted at retirement (when the Company’s Director or Executive Officer retires from his/her position).
- (i) Basic compensation
c. Method of setting compensation levels and compensation composition ratios
- The compensation levels and compensation composition ratios of Directors and Executive Officers are set each year according to their roles and responsibilities based on a comparison with market compensation levels using compensation survey data of external professional organizations. When comparing with market compensation levels, major domestic manufacturers similar to the Company in terms of scale, type of business, global expansion, etc., are selected as the compensation benchmark group.
- (a) Directors
The basic compensation levels of Directors are set in consideration of the compensation levels of non-executive internal directors and Outside Directors of the compensation benchmark companies, their roles and responsibilities, and other factors. - (b) Executive Officers
The compensation, etc. of Executive Directors is set in consideration of the trends in compensation levels of executive officers at the compensation benchmark companies, the management strategy and business environment of the Company, the objectives of incentive compensation and the degree of difficulty in achieving the targets, the roles and responsibilities of the Executive Officer concerned and other relevant factors. Additionally, from the perspective of pay-for-performance, the compensation composition has been set with a higher ratio of incentive compensation to place greater emphasis on the link between performance and the medium- and long-term improvement of corporate value and shareholder value.
d. Compensation governance
- As a Company with a Three-committee system, the Company has set forth the following:
- The major roles and authority of the Compensation Committee
The Company’s Compensation Committee has the authority to determine the details of compensation, etc. for individual Directors and Executive Officers of the Company. It mainly determines the policies for determining executive compensation, etc., the details of compensation, etc. for individual Directors and Executive Officers, company-wide performance evaluations related to the incentive compensation of Executive Officers, and the individual evaluations of Executive Officers. The composition of the Compensation Committee, which is to be chaired by an Outside Director. - Decision-making process and annual schedule
In the deliberation and determination of the policy for determining executive compensation, etc., the Company’s Compensation Committee gathers information and receives advice from compensation consultants from an external professional organization with abundant global experience and knowledge, from the standpoint of ensuring independence of its judgement and enhancing the effectiveness of the roles and authority of the Compensation Committee. The Compensation Committee conducts deliberation and determination based on such information as well as due consideration of the environment and general trends surrounding the compensation for management.
e. Stock ownership guidelines
- We believe it is important to ensure that our Executive Officers share the same value with our shareholders on a long-term and sustainable basis. To this end, we have established the following stock ownership guidelines and require Executive Officers to continuously hold the Company’s stock during their term of office, even after the target amount has been reached.
- 〔Stock Ownership Guidelines〕
Targeted holdings to be achieved within four years of assuming the position
| Position | Target Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| President & CEO | The multiple to be applied to the annual basic compensation | 1.3 times |
| Executive Vice President | 1.1 times | |
| Senior Vice President | 1.0 times | |
| Executive Officer | 0.8 times | |
f. Malus and clawback provisions
- The Company shall introduce “malus and clawback provisions” so that, in the event of any material misconduct or violation by an Executive Officer, or in the event of any material revision to the financial results of prior fiscal years, the Compensation Committee may, by resolution, demand that such Executive Officer forfeit his/her right to receive incentive compensation (malus) or return his/her paid compensation (clawback). The compensation that may be subject to these provisions shall be performance-based bonuses to be paid or already paid, points granted before the delivery of shares and shares before the lifting of transfer restrictions, and some or all of the shares already delivered.
Regarding Outside Directors
Outside Directors
The Company has six Outside Directors, each of whom has no special interest with the Company. Although companies which each of the Outside Directors holds office in or has been a director or officer of include those with trading relationships with the Company, no such relationships have an impact on the independence of each relevant Outside Directors based on the scale or nature of such trading, and thus they possess no risk of giving rise to any conflict of interest with the general shareholders of the Company.
Outside Directors are expected to supervise management from a high-level perspective based on their abundant experience. Those who are comprehensively judged to possess the character, acumen, and business and professional experience suited to fulfill that role, and who satisfy the requirements of independent executives specified by the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the requirements specified in Mitsubishi Electric’s Guidelines on the Independence of Outside Directors (see note at below) and thus possess no risk of giving rise to any conflict of interest with the general shareholders of the Company, are selected as Outside Directors.
<Independency Guideline for Outside Directors>
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation nominates persons with experience in company management in the business world, attorneys and academics, among other specialists, who are appropriate to oversee the Company’s business operations and not falling under any of the following cases, as candidates for Outside Directors. Each of the following 1, 2, 4 and 5 includes a case in any fiscal year during the past three fiscal years.
- Persons who serve as Executive Directors, Executive Officers, managers or other employees (hereinafter “business executers”) at a company whose amount of transactions with the Company accounts for more than 2% of the consolidated revenue of the Company or the counterparty
- Persons who serve as business executers at a company from which the Company has borrowings that exceed 2% of the consolidated total assets
- Persons who are related parties of the Company's independent auditor
- Persons who receive more than 10 million yen of compensation from the Company as specialists or consultants
- Persons who serve as Executive Officers (Directors, etc.) of an organization to which the Company offers contribution that exceeds 10 million yen and 2% of the total revenue of the organization
- Persons who are the Company's major shareholders (holding more than 10% of voting rights) or who serve as their business executers
- Persons who are related parties of a person or company that have material conflict of interest with the Company
In addition, Outside Directors enhance the checking function of management by receiving reports about the activity status of internal auditors, the audit committee, Independent Auditors, and divisions in charge of internal control via the Board of Directors, and providing valuable comments regarding Mitsubishi Electric’s management from an objective perspective. By doing this, they bring greater transparency to the management framework and strengthen the Board's function of supervising management.
Outside Directors (as of June 25, 2024)
| Name | Positions Held | Reasons for Nomination | Board Attendance Rate (FY2024) |
|---|---|---|---|

Tatsuro Kosaka |
Chairperson of the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee | Mr. Kosaka’s experience and insights as a business specialist cultivated over the course of his career in management of a manufacturing company are highly beneficial to Mitsubishi Electric. Serving as Outside Director of the Company since June 2022, he has overseen the Company’s business operations, and he is also currently making efforts for various activities as Chairperson of the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee. The Company expects him to oversee the Company’s business operations, by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of corporate management, corporate strategies and globalization, sustainability, human resources and human resources development, engineering, DX and R&D, and business development and investment at the Board of Directors and each Committee. | 100% (14/14) |

Hiroyuki Yanagi |
Chairperson of the Board of Directors, Member of the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee | Mr. Yanagi’s experience and insights as a business specialist cultivated over the course of his career in management of a manufacturing company are highly beneficial to Mitsubishi Electric. Serving as Outside Director of the Company since June 2022, he has overseen the Company’s business operations, and he is also currently making efforts for various activities as Chairperson of the Board of Directors and Member of the Nomination Committee and Compensation Committee. The Company expects him to oversee the Company’s business operations by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of corporate management, corporate strategies and globalization, sustainability, human resources and human resources development, engineering, DX and R&D, and business development and investment at the Board of Directors and each Committee. | 100% (14/14) |

Masako Egawa |
Member of the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee | Ms. Egawa’s experience and insights as a specialist cultivated over the course of her career in working at global financial institutions, research and experience in corporate governance, management experience in educational corporations, are highly beneficial to Mitsubishi Electric. Serving as Outside Director of the Company since June 2023, she has overseen the Company’s business operations, and she is also currently making efforts for various activities as Member of the Nomination Committee and the Compensation Committee. The Company expects her to oversee the Company’s business operations by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of corporate management, corporate strategies and globalization, sustainability, finance and accounting, legal affairs, compliance and governance, and business development and investment at the Board of Directors and each Committee. | 100% (10/10) |

Haruka Matsuyama |
Chairperson of the Audit Committee | Ms. Matsuyama’s experience and insights as an attorney-at-law are highly beneficial to a governance reform of Mitsubishi Electric. Serving as Outside Director of the Company since June 2023, she has overseen the Company’s business operations and she is also currently making efforts for various activities as a Chairperson of the Audit Committee. The Company expects her to oversee the Company’s business operations by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of sustainability, and legal affairs, compliance and governance at the Board of Directors and each Committee. Although she has never been involved in the management of a company other than as an outside officer before, Mitsubishi Electric has judged that she is capable of performing her duties properly as Outside Director for the above reason. | 100% (10/10) |

Kunihito Minakawa |
Member of the Audit Committee | Mr. Minakawa’s experience and insights as a management, finance and audit specialist cultivated over the course of his career, serving as Corporate Senior Vice President in charge of accounting and Auditor of a manufacturing company, are highly beneficial to Mitsubishi Electric. The Company expects him to oversee the Company’s business operations by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of corporate management, corporate strategies and globalization, finance and accounting at the Board of Directors and each Committee. | |

Peter D. Pedersen |
Member of the Audit Committee | Mr. Pedersen’s experience and insights as a global-level sustainability specialist cultivated over the course of his career, which involves working at environment and corporate, social and responsibility (CSR) consulting companies, etc., are highly beneficial to Mitsubishi Electric. The Company expects him to oversee the Company’s business operations by using a wide range of experience and insights especially in the fields of corporate management, corporate strategies and globalization, sustainability, human resources and human resources development, and business development and investment at the Board of Directors and each Committee. |
Note
- 1. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation held fourteen Board of Directors’ meetings during fiscal 2023.
- 2. The status of attendance for Mses. Masako Egawa and Haruka Matsuyama is based on the number of the Board of Directors’ meetings held after their assumed office on June 29, 2023.
- 3. Outside Directors Mitoji Yabunaka, Kazunori Watanabe and Hiroko Koide retired upon the expiration of their terms of office at the end of the 153rd Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders held on June 25, 2024.
